
Neurofeedback Therapy for autism is a non-invasive approach that harnesses brain plasticity. In this guide, we’ll explore how neurofeedback therapy works, its benefits, and steps for incorporating it into a treatment plan.
What is Neurofeedback Therapy for Autism?
Neurofeedback therapy for autism is a non-invasive treatment that aims to improve brain function and reduce autism symptoms. Based on neuroplasticity, it helps the brain change and adapt over time.
Definition and Basic Principles
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback focusing on brain activity. It involves monitoring brain waves in real-time and providing feedback to help the brain learn self-regulation.
The principle behind neurofeedback is operant conditioning. When the brain produces desirable activity patterns, it receives positive feedback, which encourages it to maintain these patterns.
How Neurofeedback Targets Autism Symptoms
Neurofeedback therapy targets specific brain function areas often atypical in individuals with autism. Many show irregular brain wave patterns related to social interaction, communication, and sensory processing.
During sessions, we focus on these brain regions. By providing feedback, we encourage the brain to adopt more typical activity patterns, potentially leading to improvements in social skills, communication, and sensory sensitivities.
It’s important to note that neurofeedback is personalized; we start with a thorough assessment and create customized treatment plans for each patient.
Benefits of Neurofeedback Therapy for Autism
Based on my experience in this medical field, I’ve observed numerous benefits of neurofeedback therapy, which can enhance the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum.
Improved Social Interaction Skills
Neurofeedback helps the brain process social cues and respond appropriately. Many patients show increased eye contact, better understanding of social norms, and enhanced engagement in conversations, translating into more meaningful relationships.
Enhanced Communication Abilities
Neurofeedback can lead to significant improvements in communication. Non-verbal patients may begin to speak, and those with limited speech can expand their vocabulary. Improved understanding of non-verbal communication also reduces frustration and enhances quality of life.
Reduced Repetitive Behaviours
Neurofeedback helps reduce repetitive behaviours that interfere with daily activities. Patients often decrease reliance on stimming behaviours and show increased flexibility, leading to improved focus and attention.
Better Emotional Regulation
Neurofeedback can improve emotional regulation, helping individuals better process and respond to emotional stimuli. Many patients experience fewer emotional outbursts and reduced anxiety, creating a more peaceful home environment.
The Neurofeedback Process for Autism
Understanding the neurofeedback process is crucial for patients and their support networks. The therapy is comprehensive and involves several key stages.
Initial Assessment and Brain Mapping for Neurofeedback Therapy
The first step is a thorough assessment of the patient’s symptoms and medical history, which helps create a baseline understanding. Following this, we perform brain mapping using quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG), identifying areas of atypical brain function contributing to autism symptoms.
Customizing the Treatment Plan
Based on the assessment and brain mapping, we develop a personalized treatment plan that targets specific brain areas and frequencies. This plan is adjusted as treatment progresses, based on individual responses and changes in symptoms.
Typical Session Structure
A typical neurofeedback session lasts 30 to 45 minutes. We place sensors on the patient’s scalp to monitor brain activity, and the patient engages in activities that provide feedback on their brain function. Positive feedback reinforces desired activity patterns.
Duration and Frequency of Treatment
The duration and frequency of neurofeedback treatment vary. Typically, we recommend two to three sessions per week initially. Many patients see improvements after 20 to 40 sessions, but some may require more. Consistency and commitment are crucial for optimal results.
Preparing for Neurofeedback Therapy
Proper preparation is essential for the best outcomes. This involves finding the right practitioner and understanding what to expect.
Finding a Qualified Practitioner
Choosing the right neurofeedback practitioner is vital. Look for professionals with training and experience in treating autism with neurofeedback. Recommendations from parents or support groups can also be helpful.
What to Expect During Your First Visit
The initial visit usually includes a comprehensive assessment and discussions about treatment goals. A baseline EEG or qEEG may be performed, which is painless and non-invasive.
Required Equipment and Setup
Neurofeedback sessions take place in a comfortable room with a computer setup. The main equipment includes an EEG amplifier and sensors placed on the scalp. The feedback is often provided through visual or auditory cues.
Supporting Neurofeedback Treatment at Home
Supporting neurofeedback treatment at home can enhance its effectiveness. Here are some practical ways to reinforce the therapy.
Complementary Activities and Exercises
Incorporating complementary activities at home can help reinforce brain patterns encouraged during sessions. Mindfulness exercises, cognitive games, and social stories can be beneficial.
Creating a Supportive Environment
The home environment significantly impacts neurofeedback treatment. Reducing sensory overload and establishing a consistent routine can help reinforce new neural pathways.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Goals
Keeping a record of progress is essential. This can involve logs noting behaviors, mood changes, and improvements in specific areas. Regularly reviewing and adjusting goals helps align support with evolving needs.
Potential Challenges and Solutions in Neurofeedback for Autism
Challenges can arise during neurofeedback therapy. Here are some common issues and their solutions.
Addressing Sensory Sensitivities
Heightened sensory sensitivities may interfere with sessions. We often start with gradual exposure to the equipment to reduce discomfort. Using softer sensors and adjusting the room’s environment can also help.
Maintaining Motivation and Engagement
Keeping individuals engaged during sessions can be challenging. Personalizing feedback mechanisms to align with patient interests and employing a reward system can enhance engagement.
Managing Expectations and Setbacks
Setting realistic expectations is crucial. Progress can be gradual and non-linear. Establishing clear, measurable goals and regularly reviewing progress helps manage expectations effectively.
Combining Neurofeedback with Other Autism Therapies
Combining neurofeedback with other autism therapies can enhance treatment outcomes. This integrated approach allows us to address multiple aspects of autism.
Integrating with Behavioral Therapies
Neurofeedback can work synergistically with behavioral therapies. Improved attention and emotional regulation can enhance engagement in therapies like ABA and CBT.
Complementing Speech and Occupational Therapy
Neurofeedback can enhance the effectiveness of speech and occupational therapy. Improved brain function in areas related to language processing and motor control can lead to more rapid progress.
Potential Interactions with Medications
When combining neurofeedback with medications, it’s essential to monitor for interactions. Neurofeedback may reduce the need for certain medications, but changes should always be made under professional guidance.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Neurofeedback for Autism
Evaluating the effectiveness of neurofeedback is crucial. A comprehensive approach to assessment helps understand the therapy’s impact.
Measuring Progress: Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments
Quantitative assessments involve objective measurements of brain activity and autism symptoms, while qualitative assessments rely on reports from patients and caregivers.
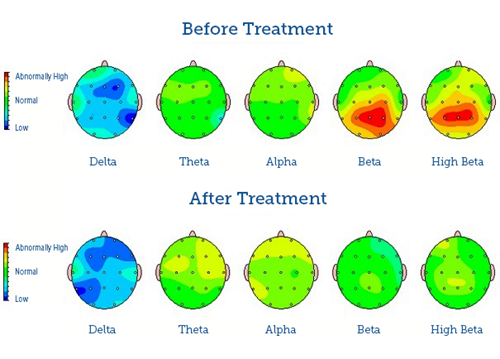
When to Consider Adjusting or Discontinuing Treatment
The decision to adjust or discontinue treatment is based on evaluating progress. If improvement plateaus, we may adjust the treatment protocol. Discontinuation is considered when treatment goals are met and sustained over time.
Long-term Outcomes and Maintenance Sessions
Long-term outcomes can vary. Many patients experience lasting improvements, while others may require maintenance sessions to sustain benefits.
Neurofeedback therapy offers a promising avenue for individuals with autism. It can lead to significant improvements in social interaction, communication, and emotional regulation. While it’s not a cure-all, many patients have experienced meaningful progress through neurofeedback.
If you’re considering this therapy for yourself or a loved one, discuss it with your healthcare team. With the right support, neurofeedback could enhance the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum. The journey towards better autism management is ongoing, and neurofeedback is one of many strategies that can help along the way. Stay open to new possibilities and celebrate small victories. Progress, no matter how gradual, is still progress.
Field Trip Health Toronto offers additional alternative treatments for treatment-resistant depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health disorders such as Stellate Ganglion Block therapy, MDMA therapy, Psilocybin therapy, and repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
About the Author

Dr. Mario Nucci MD CCFP is a licensed Family Physician with a passion for mental health and the development of new therapies. He is actively engaged in research with a faculty associate professorship at Northern Ontario School of Medicine, and research collaborations with the University of Ottawa, University of Calgary, Lakehead University, Concordia University and Vancouver Island University.
Dr. Nucci is the founder of Bay and Algoma Health Centre in 2019, a walk-in and addiction medicine clinic. He founded the Canadian Centre for Psychedelic Healing in 2019, now operating as Field Trip Health, providing cutting edge mental health care in Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Ottawa, Hamilton, Kitchener-Waterloo, Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, and at-home.