
The search for effective treatments to alcohol and substance use disorders has led to groundbreaking research in recent years, with psychedelic therapy and naltrexone both emerging as promising options. But which one is truly more effective? In this article, I’ll draw on my clinical experience and the latest scientific evidence to compare these two treatments, helping you understand their mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks in the battle against alcohol addiction.
The Science Behind Psychedelic Therapy for Alcohol Addiction
Psychedelic therapy has emerged as a promising treatment for alcohol addiction, offering a unique approach to addressing the complex brain chemistry involved in substance use disorders. I have personally worked extensively with addiction patients, and observed firsthand the potential of psychedelic therapy to create rapid and significant changes in addictive behaviours.
How Psychedelic Therapy Affects Brain Chemistry
One legal, low-dose anesthetics works by targeting the glutamate system in the brain, which plays a crucial role in learning, memory, and habit formation. When administered in controlled doses, the medicine blocks NMDA receptors, leading to increased production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). This protein helps create new neural connections, essentially rewiring the brain’s reward pathways.
In alcohol addiction, these reward pathways are often disregulated, leading to compulsive drinking behaviours. The medicine’s ability to promote neuroplasticity may help break these ingrained patterns, allowing patients to form new, healthier habits and responses to alcohol-related cues.
Potential Benefits of Psychedelic Therapy for Alcohol Use Disorder
One of the most striking benefits of psychedelic therapy is its rapid onset of action. Unlike traditional medications that may take weeks to show effects, psychedelic medicine can produce noticeable improvements in mood and cravings within hours or days. This quick response can be crucial for patients struggling with severe alcohol addiction, providing them with much-needed relief and motivation to continue treatment.
Additionally, psychedelic therapy has shown promise in reducing relapse rates. Some studies suggest that a series of infusions can help maintain sobriety for extended periods, even in patients who have failed other treatments. This could be due to the medicine’s ability to address both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction simultaneously.
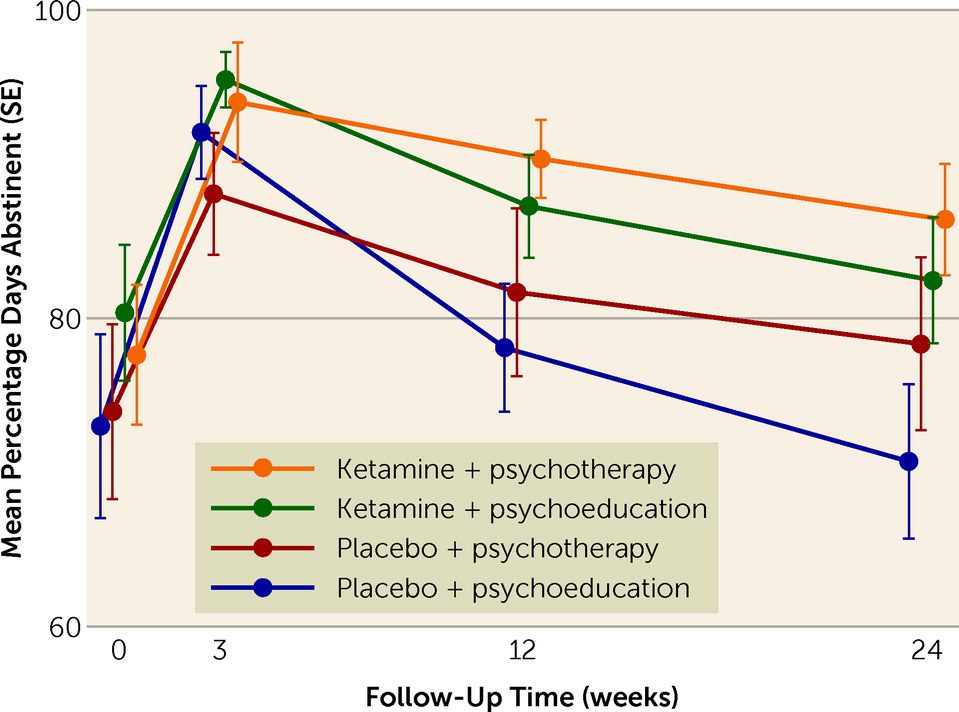
Risks and Side Effects of Psychedelic Therapy Treatment
While psychedelic therapy offers significant potential, it’s important to acknowledge the associated risks. Short-term side effects can include dizziness, nausea, and dissociative experiences. These are typically mild and resolve quickly, but they require careful monitoring during treatment sessions.
Long-term risks are still being studied, but there are concerns about potential bladder issues and cognitive effects with prolonged use. It’s crucial to emphasize that psychedelic therapy for alcohol addiction should only be administered under strict medical supervision, with careful consideration of the patient’s overall health and history. As with any powerful treatment, the benefits must be weighed against potential risks on an individual basis.
Understanding Naltrexone for Alcohol Addiction Treatment
Naltrexone has been a cornerstone in alcohol addiction treatment for decades. As a physician who has prescribed this medication to numerous patients, I’ve observed its potential to significantly reduce alcohol cravings and help individuals maintain sobriety. Let’s examine how naltrexone works and its effectiveness in treating alcohol use disorder.
Mechanism of Action: How Naltrexone Works
Naltrexone operates by blocking opioid receptors in the brain. These receptors are responsible for the pleasurable effects associated with alcohol consumption. By occupying these receptors, naltrexone effectively reduces the rewarding sensations typically experienced when drinking alcohol.
This mechanism is crucial because it helps break the cycle of addiction. When patients drink while on naltrexone, they don’t experience the same level of euphoria or satisfaction. Over time, this can lead to a reduction in alcohol cravings and consumption as the brain “unlearns” the association between alcohol and pleasure.
Effectiveness of Naltrexone in Reducing Alcohol Cravings
In my clinical experience, naltrexone has shown remarkable efficacy in reducing alcohol cravings for many patients. Studies have demonstrated that individuals taking naltrexone are more likely to remain abstinent and have fewer drinking days compared to those not on the medication.
One particularly effective approach is the Sinclair Method, which involves taking naltrexone an hour before drinking. This targeted use can help patients gradually reduce their alcohol intake over time, rather than requiring immediate abstinence. I’ve seen this method work well for patients who struggle with traditional abstinence-based programs.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
While naltrexone is generally well-tolerated, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. Common ones include nausea, headache, and fatigue. These usually subside after the first few weeks of treatment. In rare cases, naltrexone can cause liver problems, so we always monitor liver function in patients taking this medication.
Naltrexone is contraindicated for patients currently using opioids or those with acute hepatitis or liver failure. It’s crucial to have a thorough medical evaluation before starting naltrexone to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for each individual patient. As with any medication, the benefits must be weighed against potential risks on a case-by-case basis.
Comparing Psychedelic Therapy and Naltrexone for Alcohol Addiction
As a physician with extensive experience in addiction medicine, I’ve closely observed the effects of both psychedelic therapy and naltrexone in treating alcohol addiction. Each approach offers unique benefits and challenges, making it crucial to understand their comparative effectiveness, treatment protocols, and practical considerations.
Short-term vs. Long-term Effectiveness
Psychedelic therapy often produces rapid results, with some patients reporting reduced cravings and improved mood within hours or days of treatment. This quick onset can be particularly beneficial for individuals in acute distress or at high risk of relapse. However, the long-term effects of psychedelic therapy are still being studied, and maintenance treatments may be necessary to sustain benefits.
Naltrexone, on the other hand, typically requires consistent use over weeks or months to achieve optimal effects. While it may not provide the immediate relief that psychedelics can offer, naltrexone has demonstrated long-term effectiveness in reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining sobriety when used as directed. In my practice, I’ve seen patients successfully use naltrexone for years to manage their alcohol use disorder.
Treatment Protocols and Administration Methods
Psychedelic therapy usually involves a series of monitored infusions or intranasal administrations in a clinical setting. The treatment protocol often includes multiple sessions over several weeks, followed by maintenance doses as needed. This intensive approach requires a significant time commitment and close medical supervision, which can be challenging for some patients to maintain.
Naltrexone is typically prescribed as a daily oral medication or a monthly injectable form. The oral version offers flexibility, allowing for targeted use methods like the Sinclair Method. The injectable form ensures consistent medication levels and can improve adherence. Both forms can be integrated into a patient’s daily life more easily than psychedelic therapy, but they require ongoing commitment to medication adherence.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
The cost difference between psychedelic therapy and naltrexone can be substantial. Psychedelic therapy treatments are often more expensive due to the need for clinical administration and monitoring. Many insurance plans don’t yet cover psychedelic therapy for alcohol addiction, making it a significant out-of-pocket expense for most patients.
Naltrexone, being an FDA-approved medication for alcohol use disorder, is generally more affordable and widely covered by insurance plans. This makes it a more accessible option for many patients, especially those requiring long-term treatment. However, it’s important to note that the overall cost of treatment should include considerations for potential relapses and the need for additional support services, which can vary between these two approaches.
Personalized Treatment Approaches: Psychedelic Therapy vs Naltrexone
In my years of treating alcohol addiction, I’ve learned that no single approach works for everyone. The choice between psychedelic therapy and naltrexone often depends on individual patient factors. Let’s explore how we can tailor these treatments to achieve the best outcomes for each person struggling with alcohol use disorder.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choice
When deciding between psychedelic therapy and naltrexone, we consider several key factors. The severity of the addiction plays a crucial role. For patients with severe, treatment-resistant alcoholism, psychedelic therapy’s rapid effects might be more beneficial. Those with milder forms or early-stage addiction may find naltrexone sufficient.
We also look at the patient’s medical history. Liver health is particularly important for naltrexone use, while cardiovascular conditions might influence eligibility. Psychiatric comorbidities, such as depression or anxiety, can sometimes make psychedelic therapy a more attractive option due to its potential mood-boosting effects.
Combining Therapies: Potential Synergistic Effects
In some cases, combining psychedelic therapy and naltrexone can offer synergistic benefits. Psychedelic therapy might provide initial relief from cravings and improve mood, while naltrexone offers ongoing support to maintain sobriety. This combination can be particularly effective for patients who have struggled with traditional treatments alone.
However, it’s crucial to approach combination therapy cautiously. We must carefully monitor for potential interactions and adjust dosages accordingly. The timing of each treatment is also critical – for example, starting with infusions followed by oral naltrexone once the patient stabilizes.
Importance of Medical Supervision and Monitoring
Regardless of the chosen treatment, close medical supervision is essential. For psychedelic therapy, we monitor vital signs and mental state during each session. With naltrexone, regular liver function tests and check-ins to assess medication efficacy are crucial.
Ongoing psychological support is equally important. Both treatments work best when combined with therapy or counselling to address the underlying causes of addiction. We often incorporate cognitive-behavioural therapy or motivational enhancement therapy to complement the medical approach, ensuring a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each patient’s needs.
Future Directions in Alcohol Addiction Treatment
As a physician at the forefront of addiction medicine, I’m excited by the rapid advancements in our understanding and treatment of alcohol use disorder. The future holds promising developments for both psychedelic therapy and naltrexone, as well as entirely new approaches that could revolutionize how we tackle this challenging condition.
Emerging Research on Psychedelic Therapy and Naltrexone
Current research is exploring innovative ways to enhance the effectiveness of psychedelic therapy and naltrexone. For psychedelic therapy, studies are investigating optimal dosing schedules and delivery methods to prolong its benefits while minimizing side effects. Some researchers are examining the potential of oral psychedelic formulations, which could make treatment more accessible and convenient for patients.
With naltrexone, new research is focusing on genetic markers that might predict treatment response. This could allow us to personalize treatment plans more effectively, ensuring that patients receive the most suitable medication from the start. Additionally, extended-release formulations are being developed, which could improve adherence and potentially enhance long-term outcomes.
Promising Alternative Therapies on the Horizon
Beyond psychedelic therapy and naltrexone, several exciting therapies are showing potential in early trials. Psilocybin, the active compound in magic mushrooms, is being studied for its ability to reduce alcohol cravings and promote lasting behavioral changes. Early results are encouraging, suggesting it might offer a new paradigm in addiction treatment.
Another area of interest is neurofeedback therapy, which uses real-time brain imaging to help patients learn to control their cravings. This non-invasive approach could provide a valuable complement to medication-based treatments. Also, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is showing promise in reducing alcohol consumption by modulating brain activity in areas associated with addiction.
Integrating Technology and Personalized Medicine
The future of alcohol addiction treatment will likely involve a more personalized, technology-driven approach. We’re seeing the development of smartphone apps that can predict relapse risk based on behavioral patterns and provide real-time interventions. These tools could work alongside traditional treatments to offer continuous support and monitoring.
Advances in genetic testing and neuroimaging are also paving the way for more tailored treatment plans. By understanding each patient’s unique biological and psychological profile, we may soon be able to predict which combination of therapies will be most effective, significantly improving success rates in treating alcohol use disorder.
As a physician dedicated to advancing addiction treatment, I’m encouraged by the potential of both psychedelic therapy and naltrexone in addressing alcohol use disorder. While each approach offers unique benefits, the most effective treatment often depends on individual patient factors. The rapid onset of legal psychedelic medicine’s effects can provide crucial relief for those struggling with severe addiction, potentially breaking the cycle of compulsive drinking more quickly than traditional methods. On the other hand, naltrexone’s well-established track record and easier integration into daily life make it a valuable tool for long-term management of alcohol cravings. Ultimately, the future of alcohol addiction treatment lies in personalized approaches that may combine multiple therapies. As we continue to explore innovative solutions like psilocybin and neurofeedback, we’re moving closer to more effective, tailored treatments for each individual battling substance use disorders. For those seeking alternative solutions, it’s crucial to work closely with a knowledgeable healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. With ongoing advancements in the field, there’s reason for optimism in our fight against alcohol addiction.
Field Trip Health Toronto offers additional alternative treatments for treatment-resistant depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health disorders such as Stellate Ganglion Block therapy, MDMA therapy, Psilocybin therapy, Neurofeedback therapy and repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
About the Author

Dr. Mario Nucci MD CCFP is a licensed Family Physician with a passion for mental health and the development of new therapies. He is actively engaged in research with a faculty associate professorship at Northern Ontario School of Medicine, and research collaborations with the University of Ottawa, University of Calgary, Lakehead University, Concordia University and Vancouver Island University.
Dr. Nucci is the founder of Bay and Algoma Health Centre in 2019, a walk-in and addiction medicine clinic. He founded the Canadian Centre for Psychedelic Healing in 2019, now operating as Field Trip Health, providing cutting edge mental health care in Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Ottawa, Hamilton, Kitchener-Waterloo, Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, and at-home.